
Introduction:
The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the way we live, work, and communicate. It has transformed traditional industries by creating new opportunities for innovation, automation, and optimization. However, IoT devices require a reliable and secure communication infrastructure to transfer data over long distances.
What exactly is LoRaWAN?:
LoRaWAN is a low power, long-range wireless communication protocol designed for IoT devices & applications. It provides a cost-effective and efficient way to connect IoT devices over long distances. In this blog, we will discuss the best practices for using LoRaWAN gateway in your IoT devices, along with some real-world examples.
Best Practices for Using LoRaWAN IoT Applications
- Right Frequency
- Perfect power use
- Network Security
- Reliable Hardware
- Range tests
Choose the Right Frequency Band:
LoRaWAN gateway operates on different frequency bands in different regions. It is important to choose the right frequency band based on the location of your IoT devices and the regulatory requirements of that region. In the US, LoRaWAN operates on 915 MHz band, while in Europe it operates on 868 MHz band. Choosing the right frequency band ensures that LoRaWAN IoT applications can communicate effectively over long distances.
Optimize Power Consumption:
LoRaWAN gateway is designed for low-power applications, and it is essential to optimize the power consumption of your IoT devices. You can achieve this by using low-power microcontrollers, minimizing the transmission frequency, and enabling sleep modes when the device is not in use. This will ensure that your LoRaWAN IoT applications have a longer battery life and can operate without frequent maintenance.
Secure Your Network:
LoRaWAN gateway provides built-in security features, such as encryption and message authentication, but it is essential to secure your network at all levels. You can use secure gateways, encrypt data at the application level, and use strong authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access. A secure network will protect your IoT devices and data from potential threats and ensure the privacy of your users.
Use Reliable Hardware
LoRaWAN IoT applications & devices should be reliable and durable to ensure a stable and consistent network. You can choose hardware from reputable vendors and test the devices before deploying them in your network. Reliable hardware ensures that your IoT devices operate smoothly and avoid potential failures that could impact your operations.
Conduct Range Tests:
LoRaWAN gateway has a long-range capability, but the actual range may vary depending on the environmental factors and interference. You should conduct range tests to determine the actual range and optimize your network accordingly. This will help you identify the optimal placement of your gateways and IoT devices to ensure maximum coverage and avoid interference.
Real-World Examples for LoRaWAN IoT Applications:
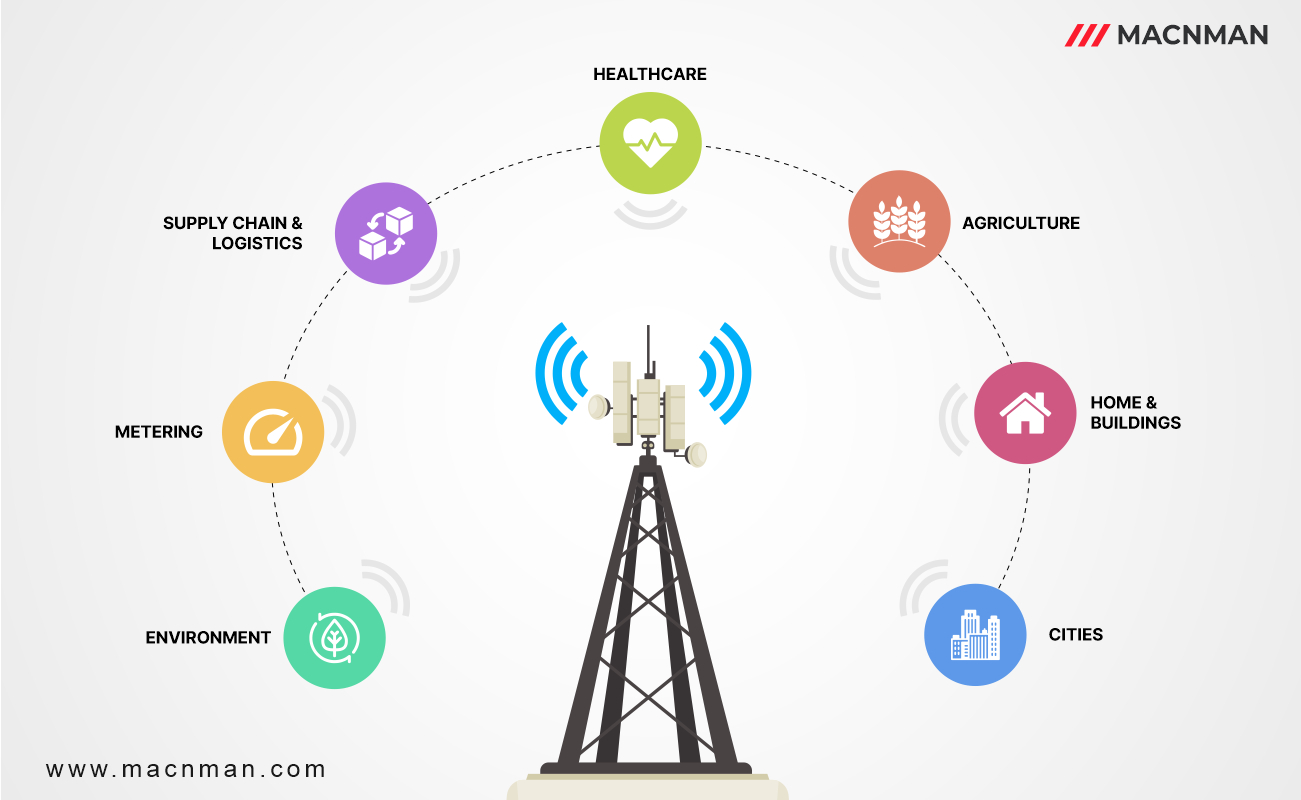
Smart Cities and Urban Infrastructure:
- Smart lighting systems for energy savings and improved safety
- Smart parking systems for reduced traffic congestion and emissions
- Smart waste management for optimized waste collection routes and reduced environmental impact
- Air quality monitoring for improved public health and environmental management Water management for efficient use and conservation of water resources
Smart Agriculture:
- Soil moisture monitoring for optimized irrigation and fertilization
- Weather monitoring for improved crop yields and protection against weather-related risks
- Livestock tracking for optimized feeding, breeding, and healthcare management
- Crop monitoring for early detection of pests and diseases
SLogistics and Supply Chain:
- Asset tracking for real-time visibility of goods and improved security
- Inventory management for optimized stocking levels and reduced waste
- Fleet management for improved efficiency and reduced operating costs
- Supply chain optimization for improved visibility, efficiency, and customer satisfaction
Industrial IoT devices:
- Predictive maintenance for improved equipment reliability and reduced downtime
- Condition monitoring for early detection of equipment failures and improved safety
- Asset tracking for real-time visibility of assets and improved security
- Process optimization for improved efficiency and reduced waste
Smart Healthcare:
- Remote patient monitoring for proactive healthcare management and improved patient outcomes
- Asset tracking for real-time visibility of medical equipment and improved security
- Logistics management for optimized supply chain management and reduced waste
Retail:
- Inventory management for optimized stocking levels and reduced waste
- Asset tracking for real-time visibility of goods and improved security
- Customer engagement for improved customer satisfaction and loyalty
Energy:
- Smart metering for improved energy management and reduced costs
- Energy management for optimized energy consumption and reduced waste
- Renewable energy monitoring for improved performance and efficiency
Security:
- Asset tracking for real-time visibility of assets and improved security
- Surveillance for improved safety and security
- Intrusion detection for early detection of security breaches
Conclusion
In conclusion, LoRaWAN technology has found extensive application across various industries due to its long-range communication, low power consumption, and low-cost infrastructure. The LoRaWAN IoT applications offer a cost-effective solution for IoT deployments using LoRaWAN gateways, enabling efficient management of resources and improved operational efficiency. With its versatility, LoRaWAN technology is expected to continue to find new applications across various industries in the future.