
What is LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN is the protocol and system architecture for the network, while LoRa module helps establish a long-range communication link. It also manages communications frequencies, data rate, and power for all nodes in the network. These nodes are asynchronous, they send when they have new information to transmit. Multiple lorawan gateways pick up their signals and forward them to a central network server while application servers take care of processing and relaying data onwards. In general it demonstrates great reliability even under moderate load; however some issues with sending acknowledgements have been observed. In this blog, we will explain what LoRaWAN & LoRaWAN gateway is, how it works, and why it is crucial for IoT
How does the LoRaWAN Gateway Works?
LoRaWAN stands for Long Range Wide Area Network. It is a low-power, wide-area network (LPWAN) protocol that uses chirp spread spectrum (CSS) modulation to enable long-range communication while consuming very little power. This makes it ideal for IoT devices that need to transmit data over long distances and operate on a battery for extended periods of time.
The LoRaWAN protocol operates on different frequency bands, depending on the region. For example, in the US, it uses the 915 MHz band, while in Europe; it uses the 868 MHz band. This enables LoRaWAN gateway to comply with local regulations and avoid interference with other wireless networks.
LoRaWAN operates on a star network topology, with gateways acting as a central hub that receives data from nearby lorawan IoT devices and forwards it to the internet. The gateways are connected to the internet via a wired or wireless network, such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or cellular.
One of the key features of LoRaWAN is its ability to support both unicast and multicast communication. Unicast communication is one-to-one communication between a lorawan IoT device and a gateway, while multicast communication is one-to-many communication between an lorawan IoT device and multiple gateways.
LoRaWAN gateway also supports different classes of devices, which determine how often they can transmit data and how long they can listen for incoming data. Class A devices are the most common and are designed to conserve battery life by only transmitting data when necessary. They listen for incoming data after transmitting, but only for a limited time window.
Why is it crucial for IoT?
In today's world, the Internet of Things (IoT) is becoming increasingly important, and the need for low-power, long-range communication between IoT devices is growing. One of the key challenges of IoT is connecting and communicating with these devices, especially those that are located in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
This is where LoRaWAN IoT devices (Long Range Wide Area Network) come in. LoRaWAN is a wireless communication protocol that operates in the unlicensed radio spectrum, enabling long-range communication between devices with low power consumption. LoRaWAN's unique modulation technique, called chirp spread spectrum, allows for communication over distances of several kilometers, making it ideal for applications that require long-range connectivity.
Applications of LoRaWAN Gateway
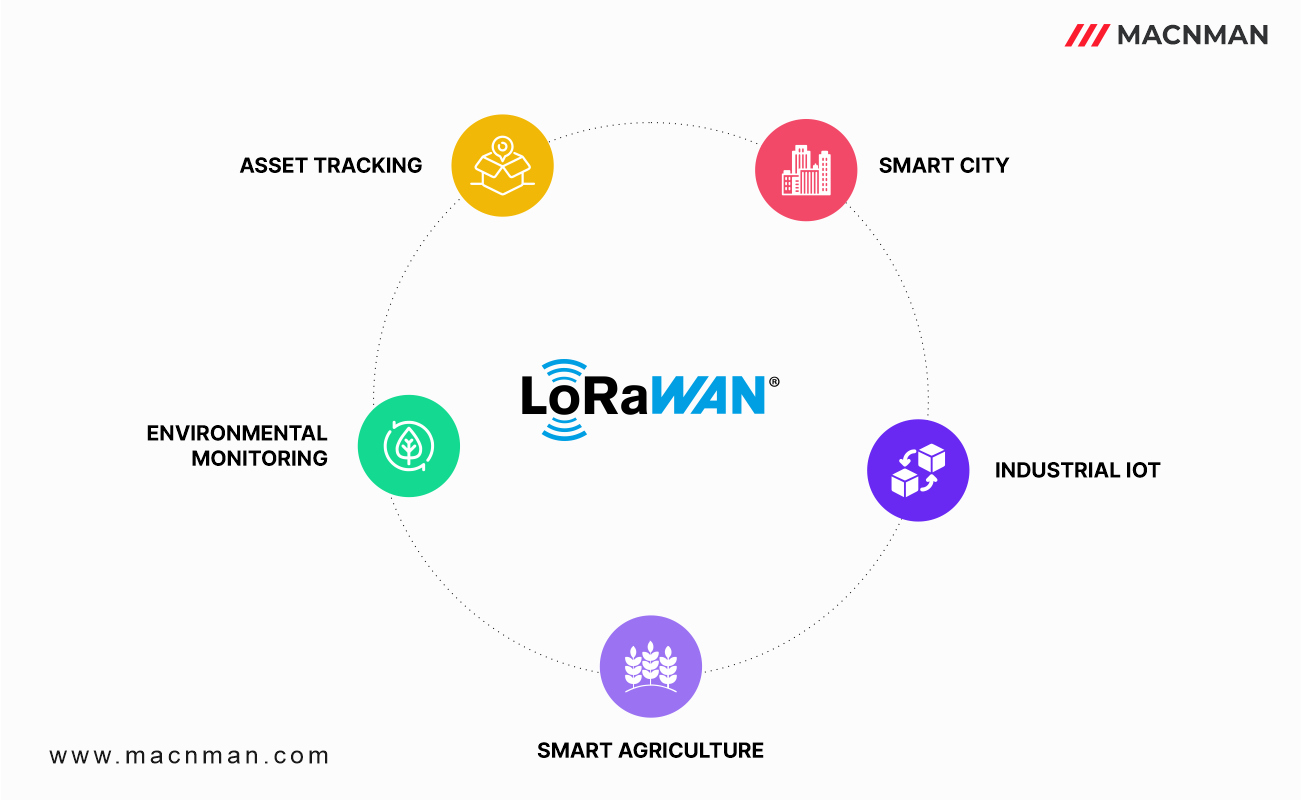
Here are some of the applications of LoRaWAN gateways:
- Smart City
- Industrial IoT
- Smart Agriculture
- Environmental Monitoring
- Asset Tracking
Smart City Applications: LoRaWAN gateways can be used in smart city applications, such as smart lighting, smart parking, and waste management. The gateways receive data from sensors placed in various locations and transmit it to the network server, enabling remote monitoring and control of the smart city infrastructure.
Industrial IoT: In the industrial IoT (IIoT) sector, LoRaWAN gateways can be used to monitor and control machines and processes in factories and warehouses. They can collect data from sensors on machines, conveyors, and other equipment, and send it to the network server for analysis and decision-making.
Agriculture: LoRaWAN gateways can be used in agriculture to monitor soil moisture, temperature, and other environmental conditions. This data can be used to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and crop growth.
Asset Tracking: LoRaWAN gateways can be used for asset tracking, such as tracking vehicles, shipping containers, and other equipment. They can receive location data from GPS trackers and transmit it to the network server for real-time tracking and monitoring.
Environmental Monitoring: LoRaWAN gateways can be used for environmental monitoring, such as air quality monitoring, water quality monitoring, and weather monitoring. They can collect data from sensors placed in various locations and transmit it to the network server for analysis and decision-making
LoRaWAN IoT devices also provide secure and reliable communication. The protocol uses advanced encryption and authentication mechanisms to ensure that data transmitted between devices is protected from unauthorized access.
Apart from the above mentioned industries, LoRaWAN gateways can also be used for waste management, and parking, where devices need to be located in remote areas and operate for long periods without maintenance. LoRaWAN gateways can also be used in agriculture for soil moisture monitoring, livestock tracking, and crop monitoring. In logistics and asset tracking, real-time location tracking, supply chain management, and inventory management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, LoRaWAN gateway is a wireless communication protocol that provides an ideal solution for low-power, long-range communication between IoT devices. It uses CSS modulation to enable long-range communication while consuming very little power. LoRaWAN operates on a star network topology, with gateways acting as a central hub that receives data from nearby IoT devices and forwards it to the internet. Its ability to support unicast and multicast communication, as well as different classes of devices, makes it flexible and scalable for a wide range of IoT applications. Therefore, LoRaWAN gateway is crucial for IoT, enabling smart cities, agriculture, and asset tracking, among other use cases.